Clinical Nutrition

- account_circleToshio HosakaMD, PhD, Prof.
- account_circleYuki ShimbaPhD, Research Asst. Prof.
- Website:https://rinshoeiyo.jimdofree.com/
- Mail:toshio.hosaka@u-shizuoka-ken.ac.jp
- Phone:+81-54-264-5567
Exploring the pathophysiological mechanism of insulin resistance and nutritional approach to diabetes managements.
Type 2 diabetes causes vascular complications and is a major public health problem associated with lifestyle diseases such as liver steatosis, hypertension, etc. Obesity is a global pandemic and, as a pathological state, is responsible for type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia and hypertension. Final goal to our research is to prevent and cure the diabetic and obesity state. And then, we are going to pursuit the following projects.
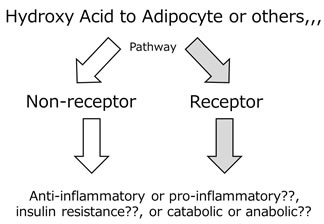
- 1. The effect of hydroxyl acid and short-chain fatty acid to insulin resistance.
Those metabolites will work or modify to cellular insulin resistance via their own receptor. However, their precise mechanism are not clear.
- 2. Nutritional management of diabetes and obesity.
Life managements such as eating habits or style, or exercise have more diverse ones. Firstly, the association of glucose fluctuation with eating habit about eating times or skipping, or preferring some components of nutrients will be examined.
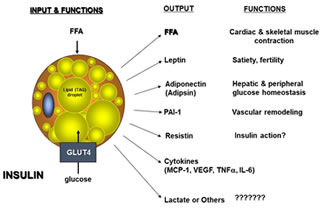
- 3. The key mechanism of early inflammation of adipocytes.
Chronic low-grade inflammation in obese adipose tissue has been proved to play crucial role in the development of obesity that induces systemic insulin resistance. We will pursuit the set point change of adipocyte’s energy storage or inflammation.
- Figure 1
- Possible mechanism of hydroxyl acid to organ
- Figure 2
- Pleiotropic effects of adipocyte.
References
- Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019 Jan 31;149:1-8.
- Physiological Reports 2018 Mar;6(5)
- Journal of Diabetes Research 2018 Mar 11;2018:9256482
- Endocrinology 153(1) 56~68 2012.
- Molecular Biology of the Cell 16 : 2882-2890, 2005